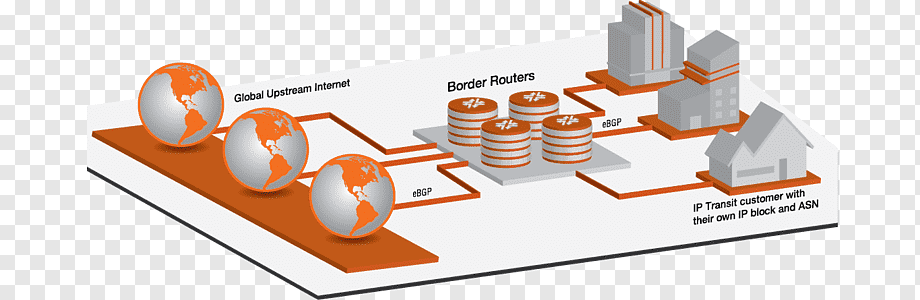
In the world of telecommunications and internet infrastructure, IP transit costs are a critical component that every internet service provider (ISP) must navigate effectively. Understanding these costs involves considering several key factors and strategic considerations to ensure optimal network performance and financial efficiency.
Understanding IP Transit Costs
ip transit costs refer to the expenses incurred by ISPs for accessing the global internet through other networks. These costs are primarily determined by the volume of data transferred (bandwidth) and the geographical scope of connectivity required. For ISPs, managing IP transit costs involves balancing bandwidth needs with cost-effective solutions.
Factors Influencing IP Transit Costs
Several factors influence IP transit costs, starting with the volume of data transferred. Higher bandwidth requirements lead to increased costs as ISPs need more extensive network resources to handle the traffic efficiently. Geographical considerations also play a crucial role, with regions lacking competition among transit providers often seeing higher IP transit costs due to limited options.
Cost Structures and Pricing Models
The structure of IP transit costs typically includes fixed costs and usage-based fees. ISPs negotiate pricing based on bandwidth requirements and contract duration. Longer-term commitments or higher bandwidth levels may result in lower per-unit costs, providing ISPs with potential savings over time.
Importance of Peering Relationships
Peering agreements between networks significantly impact IP transit costs. Peering allows ISPs to exchange traffic directly with other networks, reducing the reliance on third-party transit providers and potentially lowering costs. ISPs with robust peering relationships can optimize IP transit costs by offloading traffic onto direct connections rather than paying for transit across entire routes.
Quality of Service (QoS) Considerations
When evaluating IP transit costs, ISPs must prioritize quality of service (QoS). Factors such as network uptime, latency, and data delivery reliability influence the value ISPs derive from their transit providers. Higher IP transit costs may be justified if they ensure superior QoS, which is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and meeting SLAs.
Scalability and Future Planning
As ISPs scale their operations and anticipate future growth, IP transit costs become a crucial consideration. Planning for scalability in terms of bandwidth and geographic reach can impact negotiations with transit providers. Understanding how these factors influence IP transit costs helps ISPs make informed decisions that support long-term network expansion and financial sustainability.
Regulatory and Compliance Implications
Regulatory requirements and compliance standards also affect IP transit costs. ISPs operating across different regions must navigate varying regulations concerning data privacy, security, and network infrastructure, which can influence compliance costs and overall IP transit costs.
Conclusion
Navigating IP transit costs requires a strategic approach that considers bandwidth needs, peering relationships, quality of service expectations, scalability requirements, and regulatory landscapes. By understanding these key factors and making informed decisions, ISPs can optimize their network operations while effectively managing IP transit costs. This proactive management not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to delivering reliable internet services to customers globally, reinforcing the ISP’s position in the competitive telecommunications market.